Welcome "Harmony": A Platform Enabling Decentralized and Trustless Economies of the Future

The Strive to Create an Open Consensus for 10 Billion People ---
The concept of blockchain has become known to the world since the creation of Bitcoin by Satoshi Nakamoto in 2008. Despite the fact that decentralized money and applications are becoming widely known to the public, the main aspiration of Bitcoin has been facing some challenges brought about by limitations in its design. Other blockchain such as Ethereum that came into existence after Bitcoin has also been facing one or two challenges as a result of some certain limitations in their design. Let's quickly discuss in detail the problems of the Bitcoin and Ethereum blockchain.
- Bitcoin's Performance Bottleneck
It is no more news that the Bitcoin blockchain was originally designed to foster the initialization of peer-to-peer payment system that allows the transfer of value from one person to another without intermediaries like banks, government or payment processors. The Bitcoin blockchain gain popularity within a short period of time due to its unique features. However, as Bitcoin became known to people, the part of its performance that is too slow or cumbersome also became obviously true by simple observation as a result of its limited transaction throughput of 7 transactions per second (TPS), and its cost as a system of payment became costly to the extreme.
- Ethereum's Scalability Problem
Six years from when Bitcoin was created, A new blockchain which gives developers the opportunity to create various kinds of decentralized applications via smart contract also came into existence. That blockchain infrastructure created by Buterin and his team is known as Ethereum. Despite its unique smart contract features, Ethereum was not able to proffer solution to the problem of scalability, and its low transaction throughout of 15TPS failed to provide adequate support for applications sure as decentralized exchanges and gaming that requires high-throughput.
The quest to get a formidable proposed solution to these problems begin here...

Taking into account the limitations in the performance of Bitcoin and Ethereum, quite a good number of blockchain projects came up with their own various solutions as an attempt to bring about an increase in transaction throughput. Some blockchain proposed to use the Proof-of-Stake (PoS) consensus as a replacement for Proof-of-Work (PoW) consensus. The EOS blockchain and the likes proposed the use of Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS), where the election of block producers is done by voting instead of using the normal on-chain algorithm process. Other projects like IOTA implement the use of a DAG (Directed Acyclic Graph) data structure as a replacement for the chain-of-blocks data structure, but this could not be contained by the limitation of sequential processing of transactions.
Despite the different proposed solutions various blockchain came up with, there seems to be no significant performance gains without other important aspects such as decentralization and security being sacrificed.
This is where the Quest seems successful after the discovery of Sharding...
What is Sharding?
Sharding, which is a process which allow the creation of multiple groups (i.e shards) of validators and give them the ability to process transactions at the same time came out to be the scalability solution that preserves both decentralization and security. And as the number of shards grows, there is a linear increase in the total transaction throughput.
The first public blockchain called Ziliqa implements Sharding (but failed)...
The first public blockchain with a proposed solution to implement sharding as an answer to the problems of scalability was Ziliqa. However, the sharding approach implemented by Ziliqa proved to be less satisfactory than expected in two major ways.
- The first one being that it does not provide support for machine with limited resources to take part in the network, thus curtailing decetralization due to the reason that storage of blockchain data is not divided by this sharding approach.
- The second one is that the sharding process of Ziliqa is easily influenced or tricked by a single-shard takeover attack due to the fact that it rely on PoW as its randomness generation mechanism.
And finally, we have an answer...
The intelligent and experienced members of a team recognised the ongoing shortcomings in the Sharding approach of Ziliqa and the likes, thus, they decided to come into play and be a saviour in this situation. In their strive towards solving this, They came up with a project known as "Harmony".
This is where the real deal begins... Amiable readers, Shall I begin?
(Oh yes! I imagine you nodding in agreement) So,...

What is Harmony? ---

Harmony is the next generation blockchain powered by sharding and it is provably secure, fully scalable and energy efficient. Harmony is a consensus platform designed with the unique features of low-latency, high-throughput and low-cost needed to scale trust for billions of people and power decentralized economies in the nearest future. Harmony combines the best engineering practice and research results under the most favorable or desirable tuned system to skillfully manage and provide solutions to the problems of existing blockchains. Harmony will provide full support for applications that can not previously be done in practice on the blockchain, including interactive fair games, Internet-of-Things transactions, high-volume decentralized exchanges and Visa-scale payment systems.
The mainnet of Harmony which had 600 nodes happens to be the first fully sharded POS blockchain, and was launched on the 28th of June. Its large number of nodes made it one of the top 15 networks that is decentralized. Harmony looks forward to making an addition of 4 shards with 400 nodes each, making it a total of 1600 nodes in the phase 2 version of its mainnet. A token swap to the native ONE token, alongside the token transfers and staking smart contract will also be included in the Phase 2 of Harmony's mainnet.
Harmony is designed and built by a 12-person team which is made up of 7 engineers from Google, Apple, & Amazon and 2 PhDs.

Solutions of Harmony ---
- Efficient and Fast Consensus: Harmony is energy efficient since its consensus is powered by PoS unlike that of other sharding-based blockchains which require that the validators be selected by PoW. It takes a short time for consensus to be reached with a scalable BFT algorithm that is linear in its manner of movement and that is 100 times faster than PBFT.
- Adaptive-Thresholded PoS: As an effort to prevent stakers that are malicious from concentrating their power in a single shard, the volume of staking goes a long way to determine how much adjustment is made to the threshold of stakes that is required for a node to join the network. In order to create a fair system which gives small stakers the opportunity to participate in the network and earn rewards, the threshold is designed to be as low as possible.
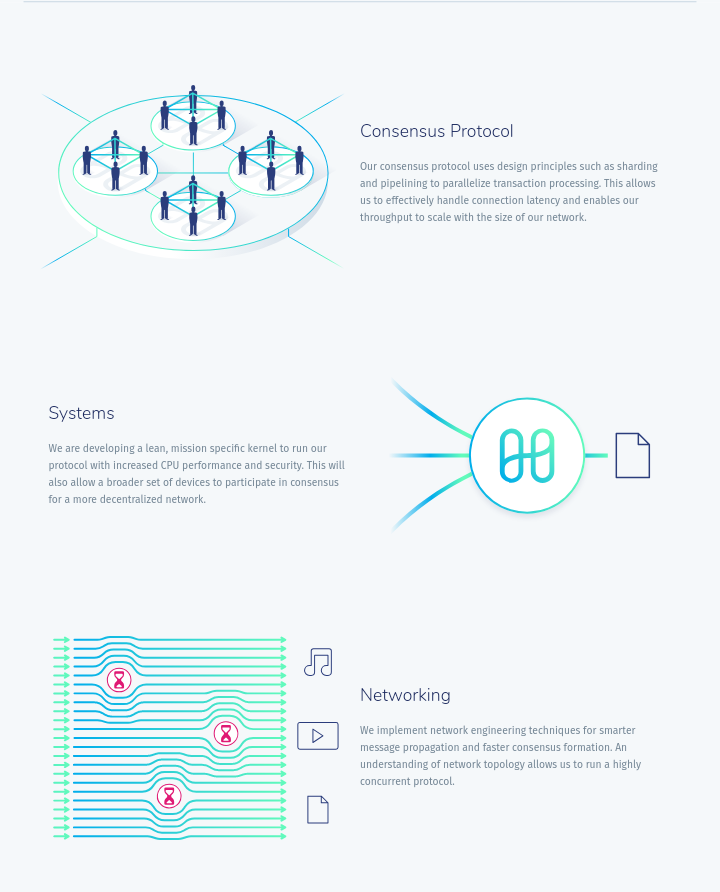
- Scalable Networking Infrastructure: By putting the Adaptive Information Dispersal Algorithm to work, the propagation of blocks within shards or across network can be achieved within a short period of time with RaptorQ fountain code. Kademlia routing is also adopted by Harmony so as to make cross-shard transactions that scale in a logarithmic manner with the number of shards an achievement.
- Consistent Cross-Shard Transactions: The direct communication of shards with each other gives Harmony the power to provide supports for cross-shard transactions. For consistency to be maintained in cross-shard transactions, an atomic locking mechanism is put in place specifically for that purpose.
- Fully Scalable: Harmony does not stop at sharding only the transaction validation and network communication like Ziliqa, but they go as far as sharding the blockchain state also. By so doing, Harmony becomes fully scalable.
- Secure Sharding: The distributed randomness generation (DRG) process of Harmony which possess the basic features of being unbiaseable, unpredictable, scalable and verifiable assist in building a provably secure sharding process for Harmony. In order to prevent the network against slowly adaptive byzantine adversaries, Harmony makes sure resharding is done for the network in a non-interruptive manner.

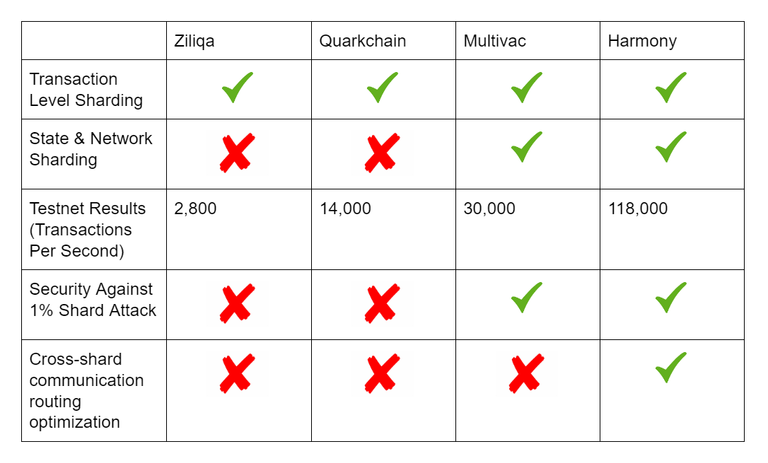
Comparing Harmony with Other Blockchain Technology ---
A PoS system which is sharded provides the best advantage or improvement that necessitates the corresponding loss or degradation between speed and fair consensus. A perfect example of such a PoS system is Harmony. A comparison of Harmony to other leading PoS blockchain projects is given here. To know more about the comparison table, check the link here.

Harmony is Saving Projects faced with Modern Scalability Issues ---
The problem of scalability is a real issue many existing projects have been struggling with. Those projects that are not struggling with the issues of scalability already are most likely to encounter the same issues in the nearest future as their project continue to grow.
Cryptokitties
Cryptokitties happens to be one of those popular great projects that amassed a large established group of users only to completely physically block the entire Ethereum network. Animoca is the company behind Cryptokitties, and they have signed a partnership deal with Harmony in order to work together to achieve a common goal of developing a new ecosystem for crypto collectibles. For more information, read about the Animoca & Harmony Partnership in detail.
DeFi (Decentralized Finance)
A report given out by Binance in the Binance DeFi Report made it known to us that DeFi has become one of the most popular use-cases of the Etherium network. DeFi is composed mainly of cryptocurrency lending and borrowing, and as a result, there is utmost need for high transaction throughput. The issues of scalability hits Etherium again in this case, as the transaction speed of Etherium network is not capable of keeping up with the demand of DeFi. There is no chance of this getting any better as the industry continues to grow. Full support can be efficiently and securely provided to the growing needs of DeFi industry by Harmony. By implementing Harmony's sharding, they are able to tolerate significant increases in throughput as the demand of a project rises, making sure that their infrastructure won't cause any part of the process to be too slow or cumbersome.

Harmony's Consensus Mechanism ---

The consensus protocol is a very important part of any blockchain. This is simply because it determines how quickly and securely the validators of blockchain reach consensus on the next block. Harmony's consensus protocol known as Fast Byzantine Fault Tolerance (FBFT), which is scalable in term of communication complexity in a linear manner is designed as an improvement on Practical Byzantine Fault Tolerance (PBFT). In FBFT, the need for all validators to broadcast their votes becomes antiquated. Instead, a multi-signature process of signing is put in place by the leader to collect the votes of all validators in a O(1)-sized multi-signature and then broadcast it. Only one multi-signature is then received by each validator as a replacement for receiving O(N) signatures, and the communication complexity is reduced to O(N) from O(N2) as against that of PBFT which is O(N2).
Harmony also improves upon the Schnorr multi-signature scheme of ByzCoin’s BFT by making use of BLS (Boneh–Lynn–Shacham) multi-signature, where only one round-trip is required. As a result of this, the speed of FBFT is at least 50% more than that of ByzCoin’s BFT. The block broadcasting process is also made faster than ever before with the adoption of RaptorQ fountain code by Harmony. The ByzCoin’s original tree-based multicasting design is also made more secure by using the fountain code broadcasting technique.
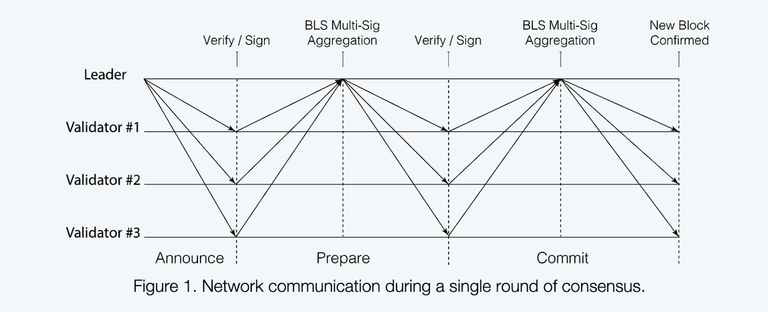
There are five steps involved in the consensus of Harmony’s FBFT, and they are as follows:
- The construction of the new block is done by the leader, after which the block header is then broadcasted to all validators. And a broadcast of the content of the block is done with erasure code at the same time. This is referred to as the announce phase.
- The validity of the block header is examined by the validators, after which it is signed with a BLS signature and sent back to the leader.
- The leader aggregates the valid signatures into a BLS multi-signature, but only after the leader has at least 2f + 1 signatures that is valid from validators (with the leader included). The aggregated multi-signature is then broadcasted alongside a bitmap that gives an indicator of the validators which have signed. This step together with step 2 make up the prepare phase of PBFT.
- The validator verify the broadcasted transactions gotten from the leader in step 1, in the block content, but this is done only after the validator is sure that the multi-signature has a minimum of 2f + 1 signers. The message received from step 3 is then signed and returned back to the leader.
- The leader aggregates the valid signatures into a BLS multi-signature, but only after the leader have waited for at least 2f + 1 signatures that is valid (can be different signers from Step 3) from step 4, after which a bitmap logging all the signers is created. Finally, the new block with all bitmaps and multi-signatures attached is made a permanent change by the leader, after which the new block is then broadcasted for all validators to commit. This step together with step 4, make up the commit phase of PBFT.

Harmony's Sharding ---
The system of Harmony is developed and designed based on inspiration drawn from both industrial and academic developments. The industry acquire the knowledge to shard from the Ziliqa network. The idea of state sharding which was developed from academic papers was used in giving correction to the storage bottleneck of the Ziliqa protocol and gave a prediction of the attack vector that might corrupt single shards gradually as the time passes. Harmony has accrued some basic knowledge from both academic and industry and those knowledge have been utilized in the development of its own sharding scheme which is linearly scaling and provably secure.
Harmony is made up of two chains which are the beacon chain and multiple shard chains. The beacon chain function as the identity register and randomness beacon. The multiple shard chain on the other hand deals with the storage of separate blockchain states and processing of transactions at the same time. A combination of Verifiable Random Function (VRF) and Verifiable Delay Function (VDF) is implemented by Harmony as a measure towards providing an algorithm that is efficient for randomness generation. PoS is also included in the sharding process by Harmony. And as a result, the security consideration of a shard is shifted to the minimum number of voting shares all the way from the minimum number of nodes
--- Randomness In The Sharding Process ---
Sharding done based on randomness happens to be the scalability solution that preserves both decentralization and security as determined by Harmony, and other academic and industry leaders, out of all the various measures (which includes location-based sharding and centrally-controlled sharding) that have been taken to assign nodes into shards. Randomness-based sharding is a type of sharding in which the sharding assignment for each node is determined by a random number selected based on mutual agreement. The random number mutually agreed upon must possess the following properties:
1. Unpredictable: Nobody should be able to make a prediction of the random number before the random number is generated.
2. Unbiaseable: The generating process of the random number should not be biasable by any of the participants.
3. Verifiable: Any observer should be able to verify the validity the random number which is generated.
4. Scalable: There is need for the randomness generation's algorithm to scale to a huge number of participants.
Harmony's approach combines an abundance of solutions from various projects such as RandHound, RapidChain, Omniledger and Ethereum 2.0 by making certain improvements on them. This is an highlight of the reasons why Harmony's approach is more advanced and far better than the approach of those projects upon which they improved.
- The DRG protocol complexity of Harmony is O(n), and its order of magnitude is at least faster than RandHound when in practice.
- Harmony's approach is unbiasable and verifiable compared to that of Rapid Chain's simpler approach of giving each participant the chance to perform VSS (Verifiable Secret Sharing).
- Harmony's approach makes good use of BFT consensus to provide finality to the random number compared to the solution of Ethereum 2.0.
These solutions deals mainly on computing, sharing, proving and securing information that are in association with the number's randomness which are generated for the assignments of the nodes.
--- Epochs ---
In Harmony, the process of consensus and that of sharding is arranged or directed to achieve a desired effect by the concept of epochs. An epoch is a time interval, determined in advance during which the condition of the sharding is fixed (for example; 24 hours) and each shards incessantly runs a process of decision-making that seeks widespread agreement with the same set of validators. There is a change in the sharding structure which is determined based on the randomness of the random number generated using the distributed randomness generation (DRG) protocol each time a new epoch begins. This helps to further improve the security of Harmony's network.
--- Resharding ---
The resharding mechanism adopted by Harmony is the type based on Cuckoo-rule. Once an epoch comes to an end, the removal of validators who withdrew their stake from the network takes effect, and new voting shares will be given to those who do not remove their stake since they are not evicted from the network. These new voting shares are assigned in a random manner to the shards whose voting shares is more than the median of the entire voting shares. Then, a random redistribution of a constant number of the voting shares from all shards directly to other half of the shards who do not have up to the median of the entire voting shares is carried out. What this means is that there is continuation in the shards of Harmony, and there is no need for it to start all over again every time an epoch comes to an end. Another thing you should take note is that the number of participants who choose not to remove their stake in the network for the next epoch has some factors related to it that causes reduction in the computational requirements. This further comes in cooperation with the concept that participants with high stakes will want to do the following.
- Make sure the system runs in an optimal manner, and
- Maintain and increase their stakes as the network see growth and more consensus is reached.

Harmony's Effective Proof-of-Stake ---
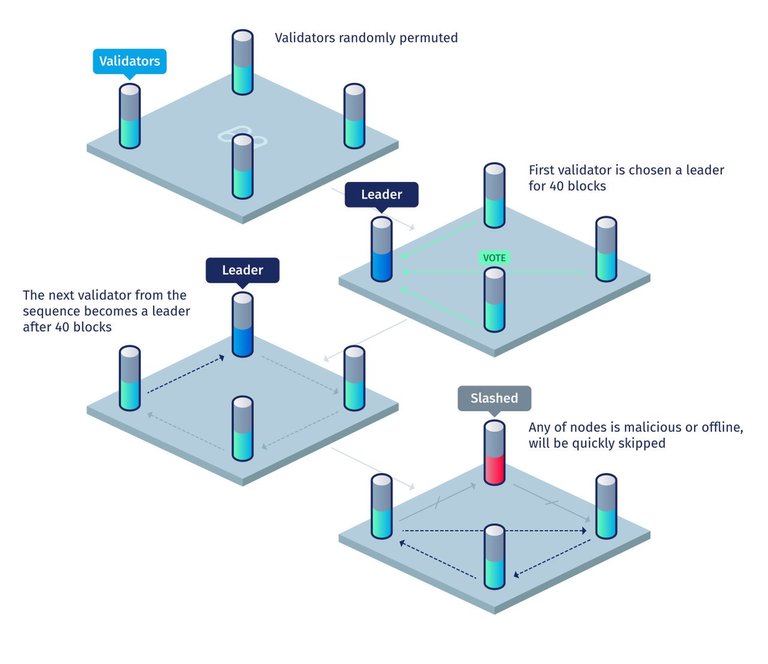
--- Electing Validators ---
It is important you know that Harmony's Effective Proof-of-Stake is used in preventing centralization. The way to distribute limited resources in the economy of Harmony can be, but not limited to, 1) by bidding or pricing, which means that whoever get it is the one that paid the highest price; 2) by social criteria, meaning the distribution is done based on title and reputation; 3) by time, how long it takes to stay in the line for an edition product that is limited; 4) or by random selection, which can be likened to a lottery. As a matter of fact, Similar method of solution is being used to select the commnunity validators. The entire team of Harmony are of the belief that the most efficient and economically secure way to elect validator is by making use of staked tokens as criteria, and this is simply because this incentivise the validators and at the same maintain the well-being of the blockchain itself. As a result, validators will be selected in Harmony's network based on the amount of stakes for its simplicity and effectiveness.
Incase you don't know, the prevention of sybil attack is a very important aspect of security that must be put into consideration in public blockchains. The method of approach selected or aproved by Harmony as the validator registration or mechanism for the prevention of sybil attack is the use of proof-of-stake (PoS). For a prospective participant to to be eligible in becoming a validator (or staker) on the Harmony's network, such validator is required to stake certain number of tokens. The number of voting shares assigned to each validator depends solely on the number of staked tokens. Each voting share gives its respective stakers the opportunity to cast one vote in the BFT consensus.
As a measure for security maintenance, malicious stakers are not allowed to be equal or more than 1/3 of the voting shares in any shard. The security of the system is further guaranteed by Harmony's adaptive threshold system. Based on the calculation given by Harmony, this system can be described as tending to withstand or survive fault if the part of the entire network that is malicious is less than ¼; which is very much conservative in the preparation for a worse-case scenario. Just as I said earlier, the highest ranked validators will be elected in Harmony's network based on the amount of stakes via their EPoS mechanism.
Specifically, for every epoch (24hours), the 1600 seats (4 shards * 400 seats) will be obtained by the top 1600 stakers, and those stakers become the validators across the shards. The validators for a new epoch is determined by the new rank of stakes once there is a change of epoch.
--- Distributing Block Rewards ---
What was proposed in Harmony's initial staking design (which is similar to the idea described in the staking model of Polkadot) is that all validators will be given equal rewards irrespective of their stakes. This model is fair in the sense that it promotes equality and help to mitigate the problem of "the rich getting richer" to some extent. This approach of equal rewards will promote the distribution of stakes evenly among validators as small stakers will have more return and big stakers will have less. The most interesting thing about this is that large stakes can be divided into small stakes such that the bearer of such large stake can act as multiple small stakers. Competitors like Cosmos are highly centralized since the top 10 validators are reportedly said to hold nothing less than 50% of the total staked token, while EOS has limited commitee seats which is 21 in number. Here is a graph showing the Effective Stake of Validatord and the Curve of Actual Stake:

--- Slashing Mechanism ---
The slashing mechanism will be used in preventing misbehavior and potential attacks from happening. Two slashing rules will be employed in Harmony's EPoS. First, the double signing slashing rule which state that there is a minimum of 2% slashing on the stake. Second, the unavailability rule which gives details concerning what will happen to validators' voting power when they are not available for some specified period of time.

Shard Chain and Beacon Chain ---
Just as I said earlier, Harmony is made up of two chains which are the beacon chain and shard chains.
The Shard Chain
A shard chain is a blockchain that deals with the storage of separate blockchain states and processing of transactions at the same time. Transaction processed by a shard are the ones relevant to the shard itself. Despite the fact that a shard chain is relatively independent, it utilizes the cross-shard communication method to communicate with other shard chains.
The Beacon Chain
The Beacon chain is one of the two types of Harmony chain. The Harmony beacon chain is a blockchain distinguished by its uniqueness, as it performs more function than the shard chain. The beacon chain can be likened to be a shard when operating or functioning. Just like other shard chains, beacon chain also deals with the processing of transactions. However, the beacon chain also perform two additional functions that are very vital.
- Generating the random number, which comes in action to determine which validators are assigned to a shard.
- Accepting the stakes of stakers who looks forward to becoming validators. In lieu of this, it is safe to say beacon chain is the chain where stakers who wants to become validators deposit their tokens. Validators for the beacon chain are determined in a way that is similar to that of other shard chains.
The block header from each shard chain when added into the beacon chain go a long way to empower the beacon chain to help fortify the cosistency and security of the states of the shard chains. Including the block headers from each shard chains into the beacon chain perform two roles:
- It makes it very difficult for a single shard to be attacked. This is because attackers will have to corrupt both the beacon chain and shard chain to make others believe that there is a valid alternative block in the shard chain.
- It also help in reducing the network cost which is used to broadcast the block headers among shards. If each shard is allowed to broadcast its headers in a separate way, then we will have a network communication of O(N^2). But the complexity of the network communication is reduced drastically to O(N) if the beacon chain act as a central relay.

Blockchain State Sharding ---
The state sharding used by Harmony is applied on account-based data model. This method of approach used by Harmony is quite effective and more efficient than the UTXO (Unspent Transaction Output) data model adopted by other state-sharding blockchains. An account state is attached to each shard chain, and all the shard benefit from all existing tokens during its distribution.The smart contract account and that of the user is treated in a different way in sharding. The account of a user is not restricted to having one same balance at different shards. What am saying in essence is that a user can have 200 tokens at shard A and at the same time have 100 tokens at shard B. A cross-shard transaction can be issued from a user-account if the such user want to move its balance from one shard to another. A smart contract account cannot go beyond the specific shard where the contract was brought into existence. In case of situations where we have dapps (decentralized applications) that requires a throughput that is much more than what a single shard can handle, Harmony has designed a decentralized application developer which is capable of creating multiple instances of the same smart contract on multiple shards and give each instances the opportunity to handle a subset of the incoming traffic. Despite the fact that these instances do not share the same state, it gives chance for communication to be carried out between the instances across shards.

Pangaea - An Experimental Game Facilitating Quality Interaction in the Harmony Ecosystem ---

Pangaea is a game built mainly to be used as an experimental zone to facilitate quality interaction between thousands of people and the Harmony network, test the limitation of Harmony's technology and have variety of fun while getting rewarded in form of cryptocurrency. The only reason Pangaea is created is to serve experimental purposes. It will be powered by its own native currency for playing and bookkeeping. Pangaea is the first live experiment displaying the potential things that may come to pass for being a part of the Harmony network as it develops. The following achievement is recorded by the Pangaea initiative within the first 24 hours:
- 138 Nodes up & running already
- 1283 Signups
- 77 Countries
- 356 Keys Downloaded
The goals of Pangaea
- Test Harmony’s upcoming core protocol milestones and updates such as staking smart contracts and resharding, on a network of all external nodes
- Set-up and onboard a vast number of nodes, ready to jump into the mainnet, through collective knowledge building and competitions.
- Identify and award community members who help secure Harmony network and are willing to go the extra mile by taking on leadership roles in our validator community More about Pangaea and how you can setup a node in our experimental zone.
To know more about Pangaea, check it out here.

Harmony and Matic comes in Partnership ---

In view of giving the best to its users, Harmony have teamed up with a leading L2 scaling solutions provider known as Matic Network. The Matic Network is built to boost scalability to a degree worth considering by leveraging an adapted version of Plasma with side chains based on Proof-of-Stake. The Integration of Harmony with Matic Network is an added advantage for Harmony's transaction speed and scalability as it becomes even faster and more improved. This partnership also stands to benefit dapps on Harmony since they can run computational task that are complex off the chain in Matic Network. And as such, they will be paying less in gas fees and also, the problem of slow performance due to heavy computational task is solved potentially. For more details, check this link.

Harmony ONE Token ---
The open and fully decentralized network of Harmony is powered by the use of their native protocol token known as Harmony ONE. The token is used in providing the participant of Harmony such as investors, developers, validators/stakers and community members who take part in developing, securing, and governing the Harmony network with incentives and rewards. Users are required to pay a small transaction fee in the form of native Harmony ONE token to be able to use the Harmony network.

Use Case ---
Prospectors is a game dApp powered by the EOS blockchain. I have been playing this game for over a month now. I was lucky to be an early adopter of this game dApp. Initially, when I started playing the game, it was very fast and slick and I really enjoyed the user experience on it. This particular game is a very interesting game that has a lot of potentials and as such, they were able to see a large influx of users within a very short time. However, as the population of users increases, the performance of the game dApp get slower.
It would have been a different case entirely if Prospectors is a game leveraging the Harmony network. This is simply because Harmony has been integrated into Matic Network and as such, dApps on Harmony do not face the risk of experiencing slow performance that may set in due to heavy computational task since they can run computational task that are complex off the chain in Matic Network. These dApps will also enjoy a mouthwatering benefit of paying less gas fee and they scale further and even faster.

More Information about Harmony token, team and roadmap is shown here:

An highlight of Harmony Technology

Final Thoughts ---
As far as I am concerned, Harmony is a unique project that have come with the right blockchain-based sharding approach to deal with the issues of scalability that have been tormenting quite a good number of blockchain based projects including Bitcoin, Ethereum, EOS, and Ziliqa. Harmony is here to bring positive changes to the blockchain industry through its uniqueness, and that is why they have attracted attention from Personalities like Vitalik Buterin (Ethereum), Zaki Manian (Tendermint), Gawin Wood (Parity Technologies), Alex Skidanov (Near Protocol) and Charles Hoskinson (Cardano’s CEO).


Do check the links below for more detaills on Harmony
- Harmony Website
- Harmony OnePager
- Harmony WhitePaper
- Harmony Medium Blog
- Harmony Telegram Group
- Harmony Twitter
- Harmony LinkedIn
- Harmony Instagram
Hi, @olasamuel!
You just got a 0.53% upvote from SteemPlus!
To get higher upvotes, earn more SteemPlus Points (SPP). On your Steemit wallet, check your SPP balance and click on "How to earn SPP?" to find out all the ways to earn.
If you're not using SteemPlus yet, please check our last posts in here to see the many ways in which SteemPlus can improve your Steem experience on Steemit and Busy.
Hey Garlam - Head of Marketing at Harmony here - really love the article and was wondering if you'd be open to more work as one of our writers!
Message me on telegram - @garlamw (and yes it is the real me - check my twitter to verify my telegram id - https://twitter.com/GarlamWon)