Harmony- A next generation public blockchain where decentralized economies can experience security, scalability, decentralization.

Introduction
With the inception of blockchain technology, the world realized the use-case of peer to peer payment. But blockchain is not just limited to that. It's like a hidden treasure in the form a technology available to us. The more you dig at it, the more valuable use case you can discover that can help mankind.
The possible use-cases are many, which can not only be cost-effective for the end-users but also can be a secure & decentralized business deal. However, the implementation of this technology is not in line with its possibility. Even though the industries recognized the decentralization, they are not satisfied with scalability. The distributed network has low transaction throughput than a centralized network. And the gap is big. The major coins like BTC, LTC, ETH still scales at a lower rate. BTC is the poster boy of the crypto economy, but the scalability does not stand with its centralized peer.
Moreover, the scalability has to come along with security and decentralization to make the fundamental composition of the blockchain strong. The available scalable blockchains are not like that.
So a viable and a general blockchain solution is long due which can guarantee security, scalability, and decentralization. But the long wait is over now and this will introduce Harmony Blockchain which is highly scalable, decentralized and secure and it uses state sharding technology to achieve its goal.

Harmony
Harmony is a secure, fast and scalable state sharding network which leverages on optimal cross-shard communication for peer to peer networking, runs through linear BFT algorithm to reach consensus, uses DRG protocol, VRF and VDF to generate randomness for assigning nodes to the shards. It is a scalable blockchain which guarantees both security and decentralization.
The high-performance protocol of multiple shards reach consensus in an efficient manner and remain integral to the Harmony network with its robust security features. In simple words, the state of different shards remain in harmony with each other, despite the fact that their state, their transaction, account balance, etc all are different, yet they are one and all.
The primary objective is to offer a scalable architecture of blockchain network with full-stack approach and by innovating every layer of blockchain and employing deep sharding in it. But it equally guarantees security and decentralization.

State Sharding
Sharding is basically called as a first layer scaling solution. A blockchain network which usually consists of a number of nodes are grouped into smaller networks or shards and those minor networks or shards process the transaction and enhance transaction throughput of the entire network. So it is obvious that the minor networks or shards process and validate different sets of transaction which is a small part of the entire transaction load of the network. But as there is a number of such small networks which simultaneously process different sets of transactions, the overall network scales at a better rate.
State sharding is a little different from the normal sharding. In the normal sharding of a network, the different shards validate different transactions but their state, i.e record keeping/storage/consensus is same. But this is not the case with state sharding. State sharding goes deep and shards the consensus layer also.
So in state sharding, the different shards possess different states and different transactions. The user account balance also varies from one shard to the other. Even the smart contract also operates differently from one shard to the other.
The shards can communicate with each other using cross-shard communication. The balances can be moved, a smart contract can run across the shards. As the structure is complex in Harmony due sharding, Harmony prefers to use Kademlia protocol which propagates through the nodes with O(log(n)) distance instead of O(n). So the message can be broadcasted faster than peer to peer protocol.
So how can a network be designed with such a complex structure, where everything varies from one shard to the other?
Yes, that is exactly what Harmony is up to. That is why it is unique, that is why it is a genuine composition.
Harmony assigns the nodes to the shards and defines a time interval known as epoch; which is a terminology used in Harmony network. Interestingly, the nodes also vary from one epoch to the other.
The nodes are randomly assigned to the shards of the network in each epoch. That random number is computed by VRF and delayed by VDF before being revealed. The delay is done particularly to check last-revealer attack. The DRG protocol governs the generation of random number based on VRF and VDF and then it is computed and committed in the block. Based on the random number, the nodes are assigned to the shards.
The random number is unpredictable, unbiaseable, scalable, verifiable.
VRF- Verifiable random number
VDF- Verifiable delay function
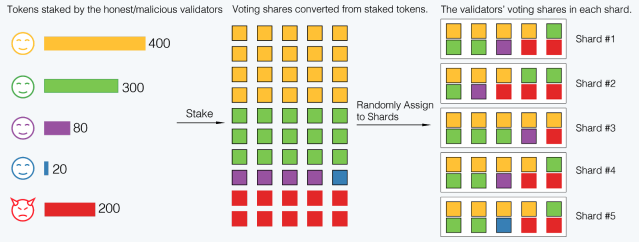
To become validators, the participants have to stake tokens in the Beacon chain and the Beacon chain also generates the random number. Those staked tokens will define their vote share in proportion to the amount of tokens staked. Then using DRG protocol, the random number is generated by the Beacon chain and based on the random number, the voting shares are assigned to the shards. So a validator will join a particular shard based on that voting share assigned.
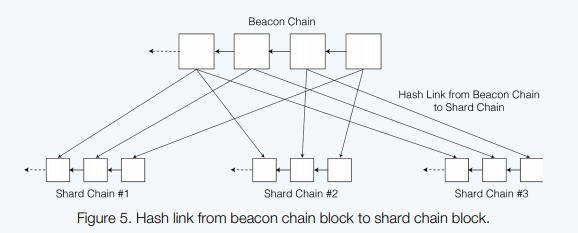
The sharding of Harmony uses the combination of Beacon chain and shard chain. The Beacon chain and shard chain are same. The Beacon chain only differs with additional roles as stated above.
So the takeaway from here is that the sharding is being done based on voting shares, not by validators. So this will fortify the sharding structure against any attack.
The cost of a voting share is determined by adaptive threshold PoS which has an equation to calculate the price of voting share and that is also not fixed, that also keep on adjusting the price so that security of the network remains intact.
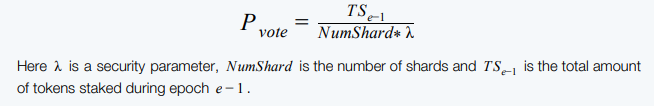
The tokens holders can delegate to different validators or to multiple validators.
Harmony uses the effective stake to evenly balance the validators in the network, otherwise big players may join as validators and start concentrating their stake in one shard, leading to centralization of stake. But they are economically discouraged to do so in Harmony. Rather the small stakers get more economic benefit.

Fast Consensus
Harmony uses BFT-Byzantine Fault Algorithm as the consensus of its network. But it has made certain modifications on PBFT; in PBFT the network complexity is O(n2). After modification by Harmony, the network complexity is O(n).
In PBFT the validator nodes rebroadcast the message(which is sent by the leader node) to all other validator nodes in the network and this is required in PBFT to count the votes. But it also makes the network complexity O(n2).
Harmony has made changes to the process of counting votes. It has introduced BLS signatures to its consensus so that the BLS signature is used by the leader to collect the votes from the validators. So using BLS signature the validators signs and send it to the leader node. The leader node collects it, aggregate it and then creates the bitmap and then broadcast it, after checking its validity it is committed in the block.
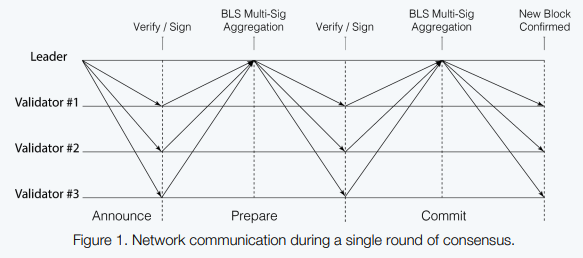
Both the leader and the validators must wait for 2f+1 signers or valid signatures before proceeding to verify or commit it.
f- Number of malicious validators.
Being the BFT algorithm, it has 'prepare' and 'commit' phase. Similarly 'leader node' and 'validator nodes'. The leader node is only one. Before the block is committed BFT consensus is run among the validators.
The advantage of using BLS signature is that it uses a single round trip, unlike schnor signature which uses two round trips. So Harmony has really innovated its consensus, first by changing the procedure of counting of votes and second by using BLS signature.

Security
(1) It uses VDF to delays the randomness, the randomness itself is unpredictable by virtue of its properties, that means no attacker can predict which nodes will be signed to which shard.
(2) The Harmony network shards by voting shares not by validators, the price of voting share is again adjusted by adaptive threshold PoS, so it is nearly impossible for the attacker to enter the network.
(3) There is a timeout mechanism in committing the randomness, so that if the randomness is not committed, it reads as if the leader has become corrupted and hence switch the leader and restart the protocol.
(4) Harmony is secure against 1% shard attack, as it does not use PoW and the design of state sharding in harmony is fortified with DRG, VRF, VDF, adaptive threshold PoS, sharding by voting shares, etc.

How can projects benefit from using Harmony as their underlying infrastructure?
For any project to thrive on the top of blockchain technology, all the three essential parameters have to be guaranteed by the underlying technology. Until now in most of the blockchain, it was a tradeoff between decentralization and scalability. Security is another important parameter.
Harmony guarantees all the three essential parameters of the underlying technology and with its state sharding, which otherwise does not affect the decentralization of the network, Harmony achieves a scalability which is at par with the centralized system. The testnet scalability figure is 118000 tps with 44000 and that is massive and a revolution. The projects can experience fast transaction throughput, low-cost transaction, a properly decentralized network and last but not the least enhanced security.

What makes sharding better than other sharding networks?
In other sharding networks, the sharding is at the transaction level, state sharding is not there. So the nodes keep on taking the entire burden of blockchain state. So more memory size required. Also, the synchronization takes a lot of time. In other networks, the network complexity is mostly O(n2) which is not linear, so the message sending and receiving is also slower. The consensus is also not linear in other networks like Zilliqa, Omniledger, etc. The scalability is also low to moderate.
Harmony is different and it is an optimized sharding network. It employs sharding at the consensus layer. So the nodes do not keep the entire blockchain state and only a small part of the state which is relevant to it is downloaded & stored by the node. Moreover, it runs through linear FBFT consensus which is fast and efficient. The communication is faster as it uses Kademlia protocol. The scalability is much higher in comparison.

What are the implications of a network that is resource efficient and linearly scalable?
Resource efficiency will bring the common man's participation. The average and simple machines can join the network. So it will be adaptable to the available resources. The resource efficiency will also help in maintaining the decentralization. Mass adoption will also accelerate.
The linear scalability is technically important for a sharded structure because the sharded structure in itself is very complex, linear scaling will make the network efficient in block propagation, message broadcasting, etc.

What are the potential applications of Harmony?
(1) Data trading platforms; using zero-knowledge proof, data can be managed and traded in an efficient manner. The scalable network of Harmony will also facilitate large B2B data trading & business compliance. Credit scoring & lending, Ad exchanges, Data marketplaces (financial, agriculture & health) are some of the use cases.
(2) Open marketplaces, gaming platform, decentralized economies of large scale, energy trading, security/asset trading, non-fungible collectibles in games, etc
(3)The supply chain can take most of the advantages of the Harmony network. The logistics and retail sector can address the issues of customers in real-time using the Harmony network. Track & trace, tracking analytics, etc can be done smoothly with Harmony network as it is highly scalable & fast.


Conclusion
There may be some existing blockchains which are scalable and addressing to specific use cases, but in a general sense, Harmony is all set for revolutionizing the blockchain technology. State sharding in itself is a revolutionary approach and now with state sharding the blockchain can be made scalable, the network can be maintained with sufficient decentralization. The design of sharding structure by Harmony is all secured. So it's a new beginning to propel scalability and decentralization both which can further bring more and more & larger projects to build the decentralized economy of the next generation.

Roadmap

Team


More Information & Resources
- Harmony website
- Harmony OnePage
- Harmony Whitepaper
- Harmony Medium
- Harmony Twitter
- Harmony LinkedIn
- Harmony Instagram
Images
- All images in this article were taken from Harmony Website.
Hello @groynes thanks for using the Realityhubs tag.
Here's the part I agree with the most concerning the potential use case of the Harmony blockchain
Indeed gaming platforms stand to gain the best by using Harmony as their underlying infrastructure also due to its high level of security, trading of fungible items will be fully supported.
Thanks for your review, we look forward to your next contribution.
Realityhubs Mod
Hello, @groynes
Thanks for your contribution. Keep up your great work.
Regards,
@anggreklestari
[Realityhubs Curator]