29-03-2024 - Economy - The market [EN]-[IT]

~~~ La versione in italiano inizia subito dopo la versione in inglese ~~~
ENGLISH
29-03-2024 - Economy - The market [EN]-[IT]
The market
Definition
We can define the market synthetically with the following sentence.
The market is the place where the supply and demand of a specific good or service meets.
Production decisions
To best manage the decision-making phases that concern the production of a company, various aspects must be considered. We can consider three of these aspects as very important:
-Life cycle of the product
-Short and long term choices
-Fixed costs and variable costs
Free competition
The main market is the free competition market. In modern economics, the free competition market is the reference market, that is, all other markets are then compared to this one in order to fully understand the nuances and differences.
How to recognize a free competition market?
A free competition market exists when the following aspects occur:
-The more similar products are offered by more companies.
-Small companies compared to the market and therefore cannot dictate the price
-Businesses can influence the consumer (loyalty)
-There must be a large sum of sellers and buyers
-Businesses can easily enter and exit the market.
free competition markets
Below are some examples of free competition markets:
-The coffee market. This market is present all over the world and is based on its high demand. Free competition is the result of its constant trade.
-The rice market. Rice is considered a universal consumer product and is made by countless companies that produce it in a very similar way. It is one of those markets that is always close to equilibrium.
-The pizza market. The pizza sector is a market with a high level of popularity, so in this case we have a high number of operators, both in terms of sellers and buyers.
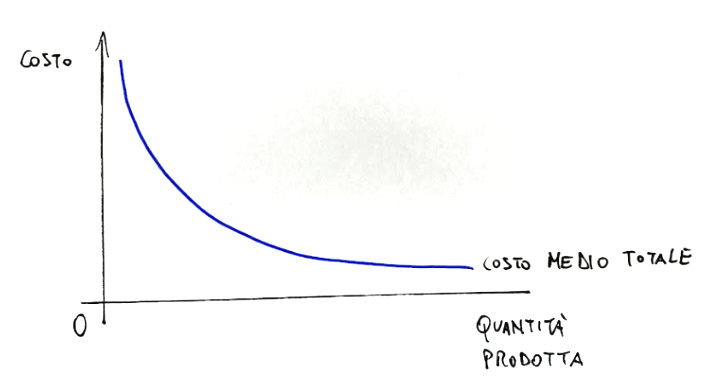
Below is a graph that shows the behavior of the average total cost of a good or service in a free competition market compared to the quantity produced.
Conditions of free competition
The conditions of free competition exist when: many companies operate in that specific market, when the objective of the companies is profit maximization, when the entry of new companies is allowed.
One thing to consider is that a condition of free competition is precisely that in the long run there is no profit.
We can summarize the conditions of free competition as follows
Conditions of free competition occur when all firms have the ability to freely enter and exit the market. In this market, companies compete with each other in offering goods or services. In this market, products or services have substitutes. In this market the consumer can view the same good or service provided by different companies and then choose to purchase it from the company that satisfies him most.
Monopoly
Monopoly occurs when the market is created by a government or external growth.
More precisely we can define monopoly as follows. It is a form of market in which there is a single seller who offers a product or service for which there are no substitutes. It is practically the opposite of free competition.
Conclusions
The markets in economics are different, but the main ones are two, the free market and the monopoly.
Request
Did you already know the difference between free market and monopoly?

ITALIAN
29-03-2024 - Economia - Il mercato [EN]-[IT]
Il mercato
Definizione
Possiamo definire il mercato in maniera sintetica con la seguente frase.
Il mercato è il luogo in cui avviene l'incontro tra la domanda e l'offerta di un determinato bene o servizio.
Decisioni di produzione
Per gestire al meglio le fasi decisionali che riguardano la produzione di un impresa bisogna considerare diversi aspetti. Tre questi aspetti li possiamo considerare come molto importanti:
-Ciclo di vita del prodotto
-Scelte di breve e lungo periodo
-Costi fissi e costi variabili
Libera concorrenza
Il mercato principale è il mercato di libera concorrenza. In economia moderna il mercato di libera concorrenza è il mercato di riferimento, cioè tutti gli altri mercati poi vengono rapportati a questo per capirne bene le sfumature e le differenze.
Come riconoscere un mercato di libera concorrenza?
Un mercato di libera concorrenza esiste quando si verificano i seguenti aspetti:
-Quanto più prodotti simili sono offerti da più imprese.
-Imprese piccole rispetto al mercato e quindi non possono dettare il prezzo
-Le imprese possono influire sul consumatore (fidelizzazione)
-Ci devono essere un'elevata somma di venditori e compratori
-Le imprese possono entrare ed uscire facilmente dal mercato.
mercati di libera concorrenza
Qui di seguito alcuni esempi di mercati di libera concorrenza:
-Il mercato del caffè. Questo mercato è presente in tutto il mondo ed è basato sulla sua forte domanda. La libera concorrenza è il risultato del suo commercio costante.
-Il mercato del riso. Il riso è considerato un prodotto di consumo universale ed è realizzato da innumerevoli aziende che lo producono in maniera molto simile. E’ uno di quei mercati che è sempre vicino all’equilibrio.
-Il mercato delle pizze. Il settore delle pizze è un mercato con un alto tasso di popolarità, quindi in questo caso abbiamo una forte numerosità degli operatori, sia per quanto riguarda i venditori che per quanto riguarda gli acquirenti.
Qui di seguito un grafico che mostra il comportamento del costo medio totale di un bene o un servizio in un mercato di libera concorrenza rispetto alla quantità prodotta.

Condizioni della libera concorrenza
Le condizioni di libera concorrenza ci sono quando: in quel determinato mercato operano molte imprese, quando l’obiettivo delle imprese è la massimizzazione del profitto, quando è consentito l’ingresso di nuove imprese.
Una cosa da considerare è che una condizione della libera concorrenza è proprio quella che nel lungo periodo non c’è profitto.
Possiamo sintetizzare le condizioni di libera concorrenza come segue
Le condizioni di libera concorrenza si verificano quando tutte le imprese hanno la possibilità di entrare e uscire liberamente dal mercato. In questo mercato le imprese competono tra loro nell’offrire beni o servizi. In questo mercato i prodotti o i servizi hanno dei sostituti. In questo mercato il consumatore può visionare lo stesso bene o servizio fornito da aziende diverse e poi scegliere di acquistarlo dall’azienda che più lo soddisfa.
Monopolio
Il monopolio si verifica quando il mercato è creato da un governo o da una crescita esterna.
Più precisamente possiamo definire il monopolio come segue. Esso è una forma di mercato nella quale è presente un unico venditore che offre un prodotto o un servizio per il quale non esistono sostituti. Praticamente è l’opposto della libera concorrenza.
Conclusioni
I mercati in economia sono diversi, ma i principali sono due, il libero mercato ed il monopolio.
Domanda
Conoscevate già la differenza tra libero mercato e monopolio?
THE END
There will always be competition in market whether people like it or not. You’ve written well
Kudos!
Thanks for leaving a comment and I agree with you…the market is what drives whether we want it to or not. In this article perhaps the most important thing is the following. All types of markets refer to the free competition market which is the basis on which the other types of markets are then differentiated
Perfettamente, il monopolio è ciò che fanno alcune comunità qui hahahaha, ed è qualcosa che non è affatto sottile.È così ovvio che non è necessario analizzare .
Scusate la risposta ma sono sincero
Gestire una piattaforma come HIVE non è affatto facile e forse in questa fase potrebbe essere facile pensare come hai pensato tu, ma io sono ottimista per quanto riguarda il futuro.
Senz'altro. Ci sono posti dove comunque il monopolio non è un intoppo, come la Norvegia.
In effetti dalla Norvegia solitamente leggo notizie positive, ma non conosco come i norvegesi gestiscono la loro economia. Oltre alla libera concorrenza ed al monopolio, io so che può esistere anche il duopolio
A noi avevano fatto studiare l'oligopolio ai tempi della scuola. Ma ovviamente anche il duopolio è possibilissimo. Una forma di oligopolio anch'essa.
I norvegesi sono esortati a seguire una filosofia egualitaria: siccome nessuno deve sentirsi superiori agli altri (pure che gli scivoloni non sono mancati: basti studiare con che naso all'insù guardavano la popolazione sami, ritenuti dai norvegesi persone di seconda e pure terza categoria sulla falsariga delle questioni razziali nazi-fasciste e bolsceviche), nessuno deve avere di più o di meno degli altri, nè case o mobilio diversi. Le abitazioni e i mobili si somigliano tutti e così pure il vestiario venduto. Fino alla marca di dentifricio. Almeno tant'è che ha illustrato una ragazza messicana che era andata a lavorare in Norvegia e ha voluto allestire una sorta di docu-reality via youtube.
Caspita! Non sapevo di questo stile di vita dei norvegesi e di questa politica
Si, pure nell'abbigliamento c'è la tendenza alla vendita di abiti uguali per tutti, sia per tipologia che colori.
Thank you so much for this quality information and knowledge you are able to share
Thanks for leaving a comment. I believe that the most important thing in this article is the concept of free competition and the conditions that identify this type of market. The conditions of free competition are:
-The objective of the company is profit maximization
-This market generates profit in the short term
There are many companies operating in this market.
-Other companies are always allowed to enter this market
-In this type of market there is no profit in the long term
see you next time
Most market that do practices monopoly to me will say it is not a wise thing to actually do