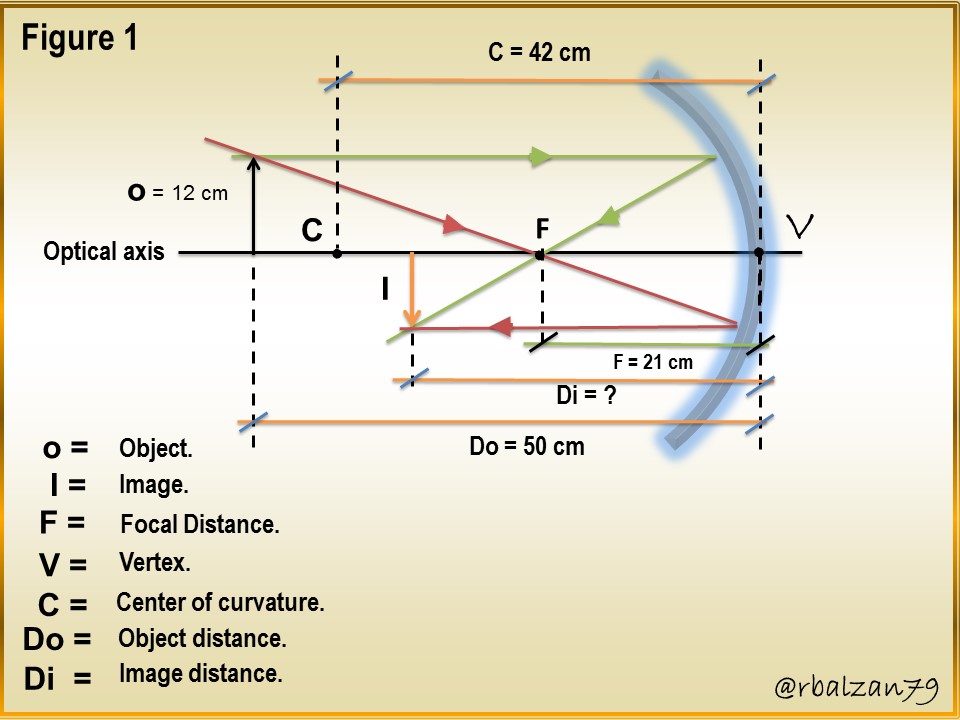
Knowing the main characteristics of the image of an object projected on a concave mirror
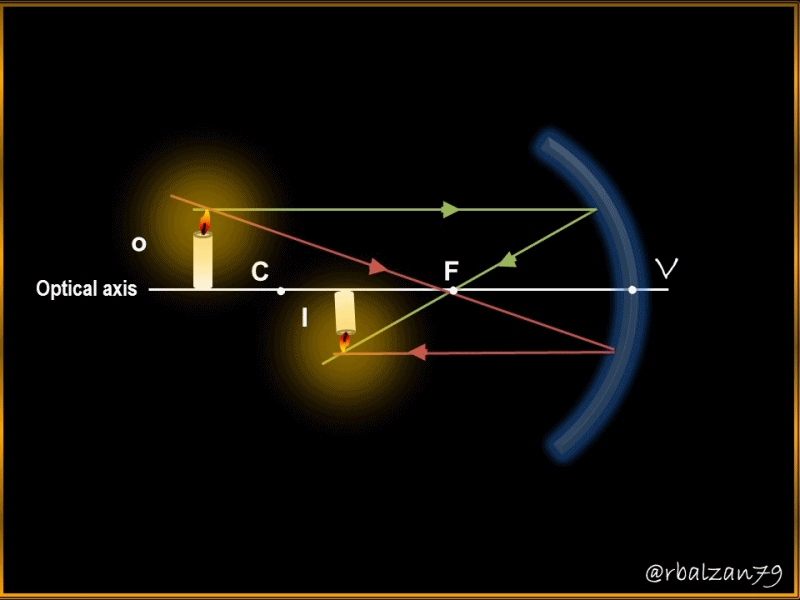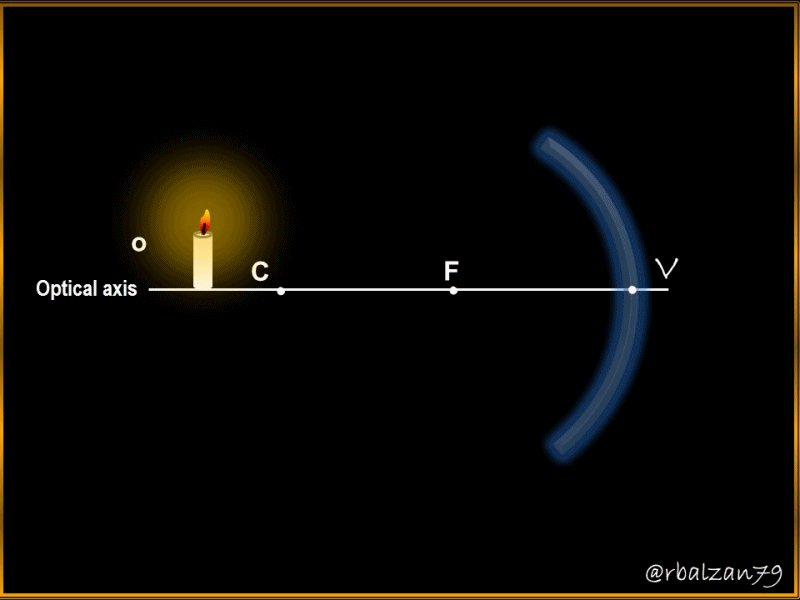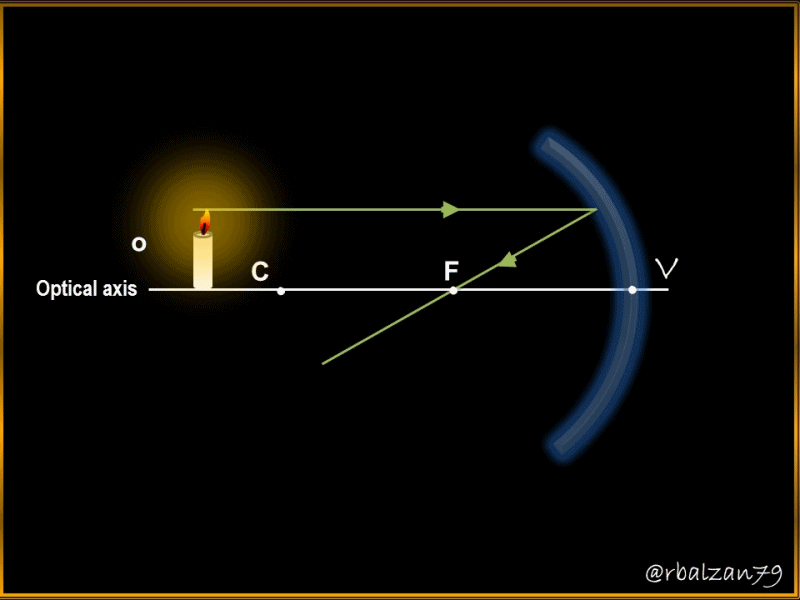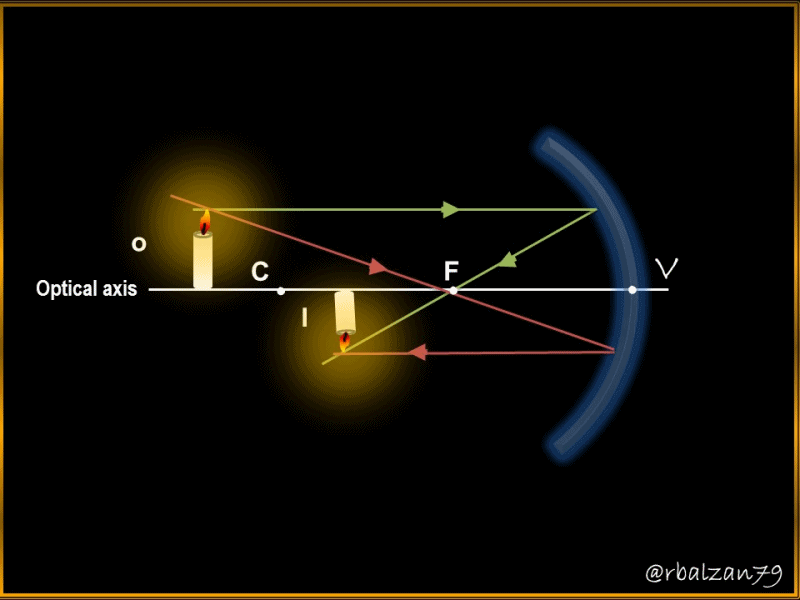
It is important to emphasize my dear readers that spherical mirrors are those that have the shape of a spherical cap, where we call radius of curvature, the radius (r) of the spherical cap, but also the center of curvature (C), the point that corresponds to the center of the sphere which is part of the aforementioned cap, as a concave mirror, another element to consider is the so-called vertex (V), and this represents the midpoint of said spherical cap, and in addition, we call main axis to that line that joins the point center of curvature (C) with the vertex (V).
An essential element to always take into account is the main focus (F), since through this point must pass all those rays that fall parallel to the main axis in the mirror once they have been reflected, but it is also important to say that the rays passing from the main focus will be reflected parallel to the main or optical axis of the mirror, therefore, the length between the vertex and the main focus (F) is called the focal length and this distance will be half the value of the radius of curvature.
Exercise
Spherical mirrors have a variety of uses in our daily life, among them, we have the concave type, where the characteristics of the image generated by the light rays will depend on the position of the body or object, therefore, let's analyze an object whose height is 12 cm and which is located at a distance of ½ meter (50cm) from a concave mirror, whose center of curvature is 42 cm, in relation to the above, answer the following question:
a.- What will be the distance of the projected or reflected image in such a concave mirror?
b.- What will be the height of the image projected or reflected in such a concave mirror?
Solución
Data:
Ao = 12 cm (Object height).
Do = 50 cm (Object distance).
C = 42 cm (Center of curvature or radius of curvature).
F = C/2 = 21 cm (Focal length).
Di = ? (Image distance).
Ai = ? (Image height).
a.- To begin to answer our first question, we must point out that in relation to figure 1, we are going to take as positive the left side, that is, the side where the real object is located:

From the above formulation of the mirrors, we proceed to clear the distance of the image (Di).
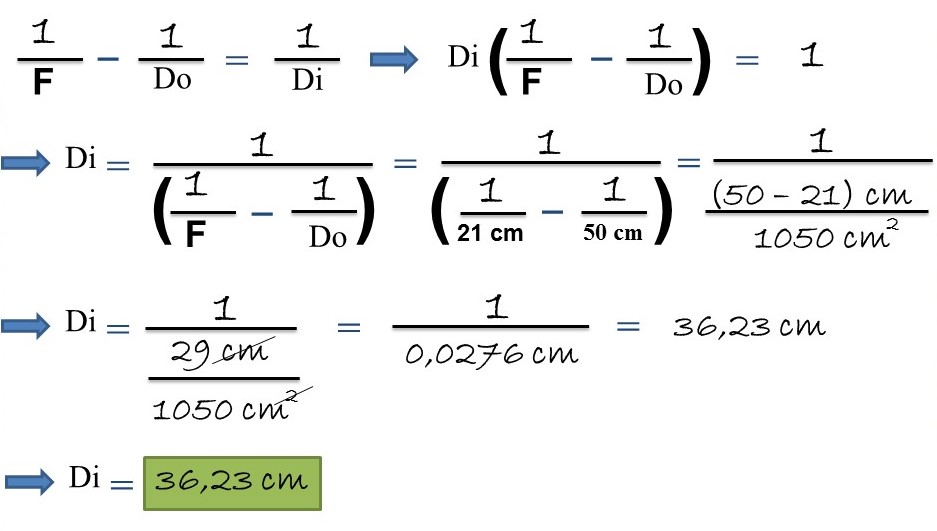
In this way we can know the distance of the image (Di) and, with positive sign, therefore, it is located according to our criterion on the same side of where the object is located, that is, on the left side, at a distance of 36, 23 cm, now we proceed to answer our second question.
b.- In order to answer this question, it is necessary to know the following formulation:
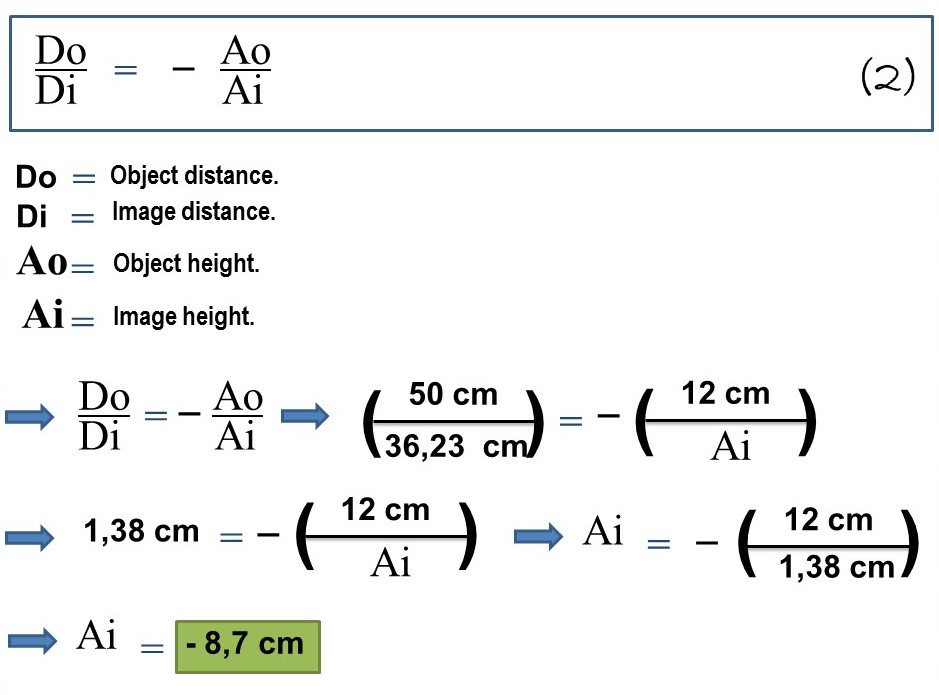
By performing the respective procedures we obtain the value of the requested variable, i.e., the height of the image (Ai) of the object reflected in the concave spherical mirror.
Conclusion
The understanding of light is one of the phenomena of greatest contribution to our evolution, thanks to its action we can witness everything that surrounds us and enjoy the wonders of our universe in full, this time we could check two simple, but significant examples of the action of light reflected in a spherical mirror with concave features.
By implementing the mirror equation or Descartes' formula we were able to calculate the distance of the image (Di) projected on the concave mirror (36.23 cm), likewise using the magnification equation we were able to know the size of the image of the object and its orientation, therefore, highlighting characteristics such as; the image is real because it originates from the same side where the object is located, it is inverted and smaller than the object.
We prove the essential usefulness of any mathematical formulation, giving us a deeper understanding of the phenomenon of light and, above all, in relation to the generation of any type of images.
Until another opportunity my dear friends.
Note: The images were created by the author using Power Point and Paint, the animated gif using PhotoScape.
Recommended bibliographic references
[1] GEOMETRIC OPTICS. Link.
[2] Ray diagram in concave mirrors. Link..
Thanks for your contribution to the STEMsocial community. Feel free to join us on discord to get to know the rest of us!
Please consider delegating to the @stemsocial account (85% of the curation rewards are returned).
You may also include @stemsocial as a beneficiary of the rewards of this post to get a stronger support.
Thank you for your valuable support. Best regards.