Antiderivatives - Examples, Part 4 - Position, Velocity, Acceleration Functions
In this video I go further into the examples series on Antiderivatives and basically show how they can be used to determine the position function when given the velocity or the acceleration functions and also initial position and velocity values. I also discuss gravity and how near the surface of the Earth the acceleration due to gravity can be taken as a constant which is equal to 9.8 m/s2 or 32 ft/s2.
Watch video on:
- 3Speak:
- Odysee: https://odysee.com/@mes:8/antiderivatives-examples-part-4-position:6
- BitChute: https://www.bitchute.com/video/XNI64dQEToTD/
- Rumble:
- DTube:
- YouTube: https://youtu.be/PDhLLURJSPs
Download video notes: https://1drv.ms/b/s!As32ynv0LoaIiZ9q6rWIgtNHIKTJMg?e=aboVRD
View Video Notes Below!
Download these notes: Link is in video description.
View these notes as an article: https://peakd.com/@mes
Subscribe via email: http://mes.fm/subscribe
Donate! :) https://mes.fm/donate
Buy MES merchandise! https://mes.fm/store
More links: https://linktr.ee/matheasy
Follow my research in real-time on my MES Links Telegram: https://t.me/meslinks
Subscribe to MES Truth: https://mes.fm/truthReuse of my videos:
- Feel free to make use of / re-upload / monetize my videos as long as you provide a link to the original video.
Fight back against censorship:
- Bookmark sites/channels/accounts and check periodically
- Remember to always archive website pages in case they get deleted/changed.
Recommended Books:
- "Where Did the Towers Go?" by Dr. Judy Wood: https://mes.fm/judywoodbook
Join my forums!
- Hive community: https://peakd.com/c/hive-128780
- Reddit: https://reddit.com/r/AMAZINGMathStuff
- Discord: https://mes.fm/chatroom
Follow along my epic video series:
- #MESScience: https://mes.fm/science-playlist
- #MESExperiments: https://peakd.com/mesexperiments/@mes/list
- #AntiGravity: https://peakd.com/antigravity/@mes/series
-- See Part 6 for my Self Appointed PhD and #MESDuality breakthrough concept!- #FreeEnergy: https://mes.fm/freeenergy-playlist
- #PG (YouTube-deleted series): https://peakd.com/pg/@mes/videos
NOTE #1: If you don't have time to watch this whole video:
- Skip to the end for Summary and Conclusions (if available)
- Play this video at a faster speed.
-- TOP SECRET LIFE HACK: Your brain gets used to faster speed!
-- MES tutorial: https://peakd.com/video/@mes/play-videos-at-faster-or-slower-speeds-on-any-website- Download and read video notes.
- Read notes on the Hive blockchain #Hive
- Watch the video in parts.
-- Timestamps of all parts are in the description.Browser extension recommendations:
- Increase video speed: https://mes.fm/videospeed-extension
- Increase video audio: https://mes.fm/volume-extension
- Text to speech: https://mes.fm/speech-extension
--Android app: https://mes.fm/speech-android
Antiderivatives - Examples, Part 4 - Position, Velocity, Acceleration Functions
Example 1
A particle moves in a straight line and has acceleration given by a(t) = 6t + 4. Its initial velocity is v(0) = -6 cm/s and its initial displacement is s(0) = 9 cm. find its position function s(t).
Solution:
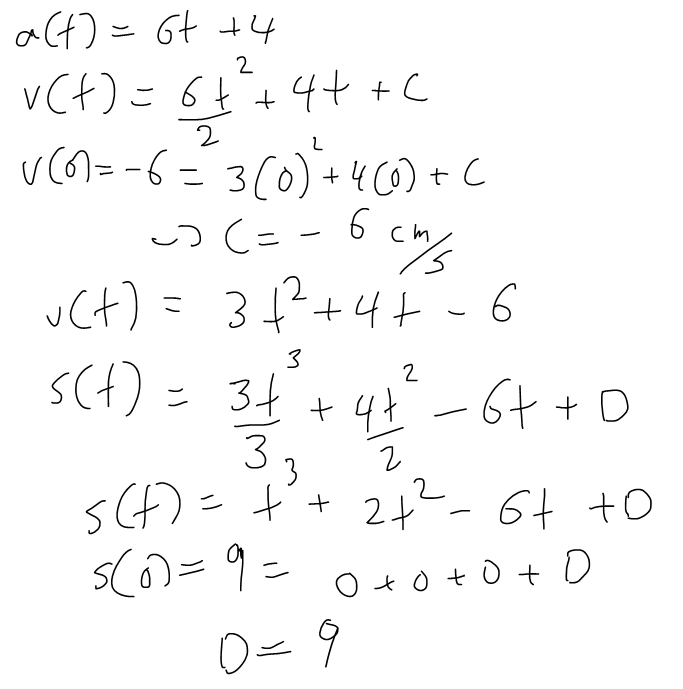
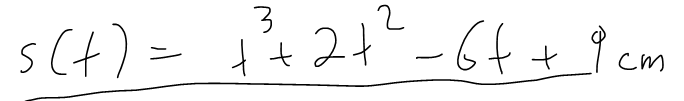
Example 2
A ball is thrown upward with a speed of 48 ft/s from the edge of a cliff 432 ft above the ground. Find its height above the ground t seconds later. When does it reach its maximum height? When does it hit the ground?
- An object near the surface of the earth is subject to a gravitational force that produces downward acceleration denoted by g.
- For motion close to the ground we may assume that g is constant, its value being 9.8 m/s2 (or 32 ft/s2)
Solution:
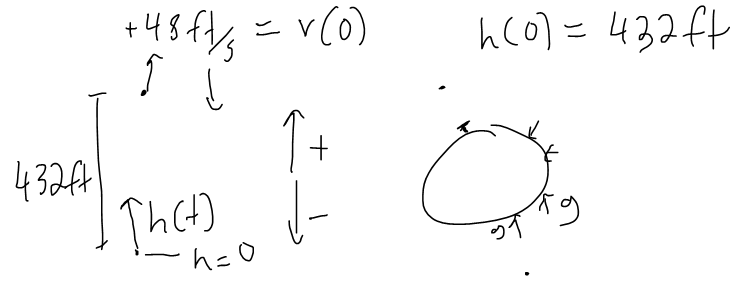
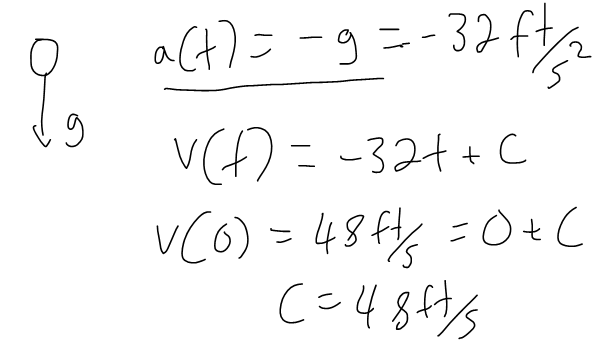
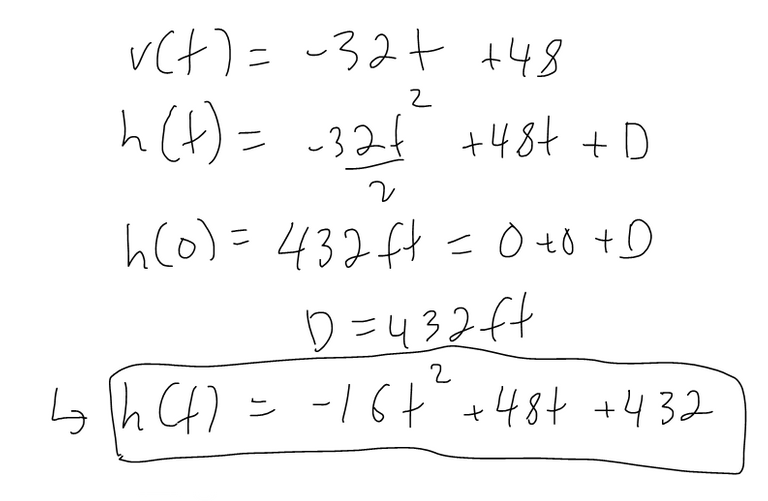
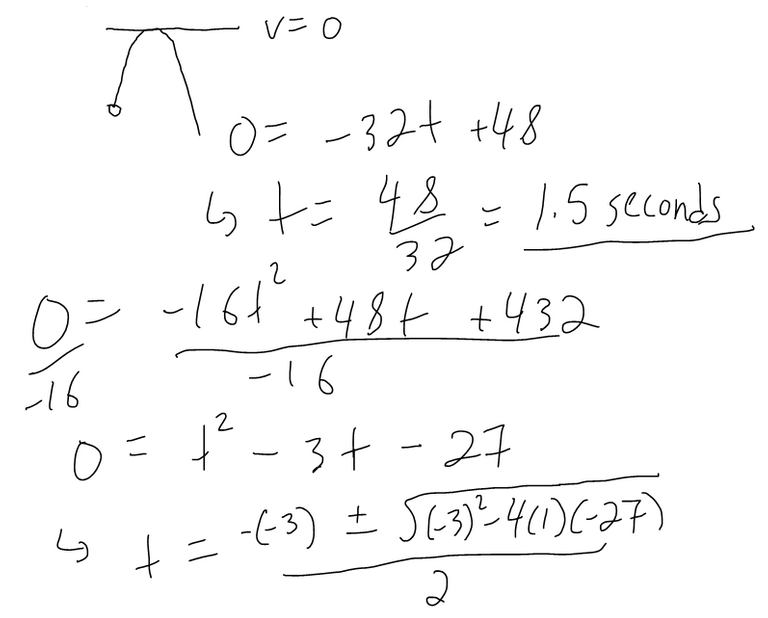
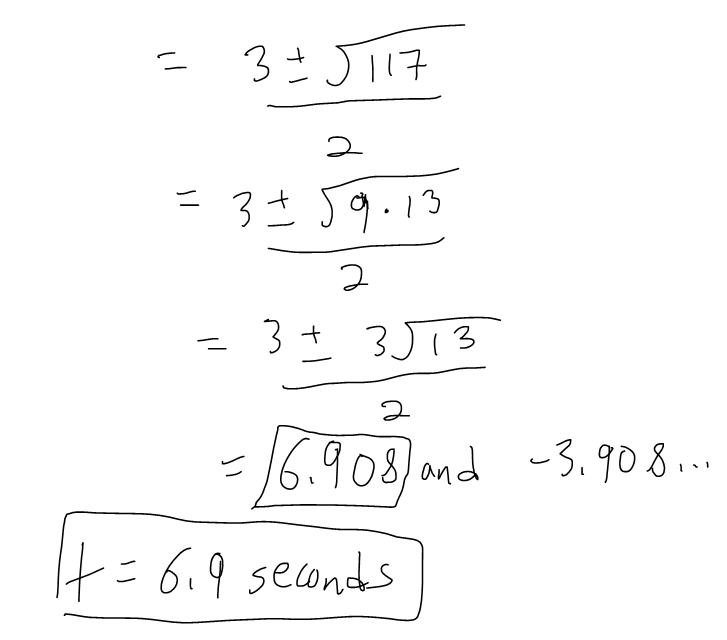
https://twitter.com/442160704/status/1590387973702684672
The rewards earned on this comment will go directly to the people( @mes ) sharing the post on Twitter as long as they are registered with @poshtoken. Sign up at https://hiveposh.com.
Nice demonstration about the problem

!1UP
You have received a 1UP from @gwajnberg!
@stem-curator, @vyb-curator, @pob-curator, @pal-curator
And they will bring !PIZZA 🍕.
Learn more about our delegation service to earn daily rewards. Join the Cartel on Discord.
Thanks for your contribution to the STEMsocial community. Feel free to join us on discord to get to know the rest of us!
Please consider delegating to the @stemsocial account (85% of the curation rewards are returned).
You may also include @stemsocial as a beneficiary of the rewards of this post to get a stronger support.
Congratulations @mes! You have completed the following achievement on the Hive blockchain and have been rewarded with new badge(s):
Your next target is to reach 85000 upvotes.
You can view your badges on your board and compare yourself to others in the Ranking
If you no longer want to receive notifications, reply to this comment with the word
STOPCheck out the last post from @hivebuzz:
Your publication has been voted by Edu-venezuela. Your post will carry over to other curation projects for more voting support. Keep up the good work!