Paleontology - study of ancient life and fossils
Introduction to paleontology
Paleontology is the study of life that existed in the past. It includes both plants and animals, as well as their fossils. The word paleontology comes from two Greek words: "palaios" meaning old, and "on" meaning being or living.
William Whewell (1794–1866) was an English polymath who contributed to many fields, including philosophy, mathematics, physics, geology and astronomy. He was also a clergyman who wrote numerous books on religion and science for general audiences. Whewell coined the term “paleontology” in 1832.
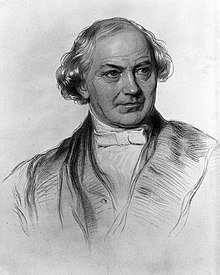
Source
Body fossils in paleontology
Fossils are important to paleontology because they allow scientists to study the evolutionary history of life on Earth. Fossils are also important for other branches of science, such as geology and paleoanthropology.
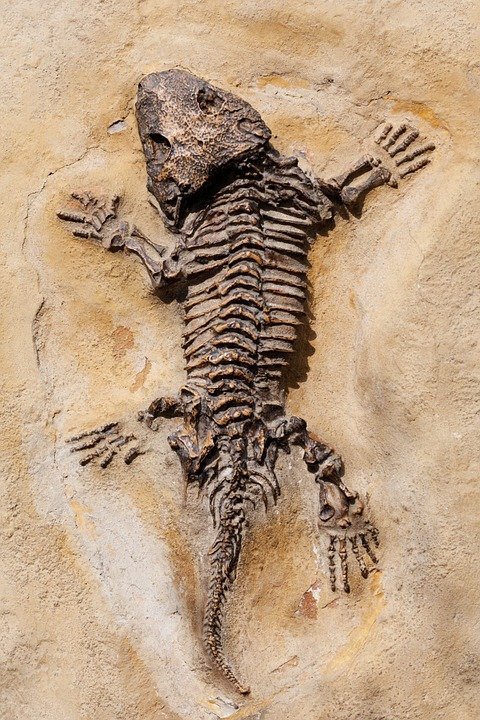
A fossil is the remains or traces of an organism preserved in the Earth’s crust, which can offer information about the age and environment in which it lived. The fossilized remains may be bones, exoskeletons, mummies, footprints or even feces. The study of fossils is called paleontology.
The oldest fossils are found in rocks that have been dated to be 3.5 billion years old. The youngest fossils are found in rocks that have been dated to be 100,000 years old.
—
Fossilization is the process of preservation of an organism, usually through mineralization. This process leaves behind a fossil or trace of the organism.
We can learn about evolution by looking at the fossils in rock layers. The fossil record is a good way to understand what life looked like in different time periods.

Source
Classifying ancient organisms
The classification of living organisms is a process that aims to organize and categorize the diversity of life on Earth. Traditionally, it was based on phenotypic traits. Nowadays, modern classification systems rely heavily on molecular and genetic evidence.
Biological classification is the taxonomic ranking of organisms based on their evolutionary relationships, with one organism being more closely related to another than to any other organism.
Cladistics is a method in biological taxonomy that groups together organisms with a common ancestor, rather than by their physical similarity.
Phylogenetic nomenclature is a system of naming organisms using clade names or node names that reflect the phylogenetic relationships between them.
History of life
The history of life on Earth is ancient, with the first life appearing at least 3.8 billion years ago. The age of the Earth is about 4.54 billion years old and the earliest evidence for life on Earth dates back to at least 3 million years ago, during the Archean era, when there was enough oxygen in the atmosphere for complex organisms to evolve.
The evolution of plants began around 450 million years ago and animals emerged around 530 million years ago during the Cambrian explosion (a period in which many new animal species appeared). The earliest fossils of animals date from 650 million years ago and trace back to a single-celled organism that lived 2 billion years before that. These simple animals evolved into more complex forms over time and eventually became fish, amphibians, reptiles and birds

Source
References
- https://www.amnh.org/explore/ology/paleontology#:~:text=Paleontology%20is%20the%20study%20of,planet%20was%20like%20long%20ago.
- https://www.britannica.com/science/paleontology
- https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/feart.2015.00009/full
- https://timescavengers.blog/introductory-material/what-is-paleontology/
It's interesting the consider how the study of paleontology and Darwin's work complemented each other as the Theory of Evolution took root. We go through periods in history when it seems certain areas of science grow contemporaneously.
Thanks for this article.