Geological and production differences between a conventional and an unconventional field
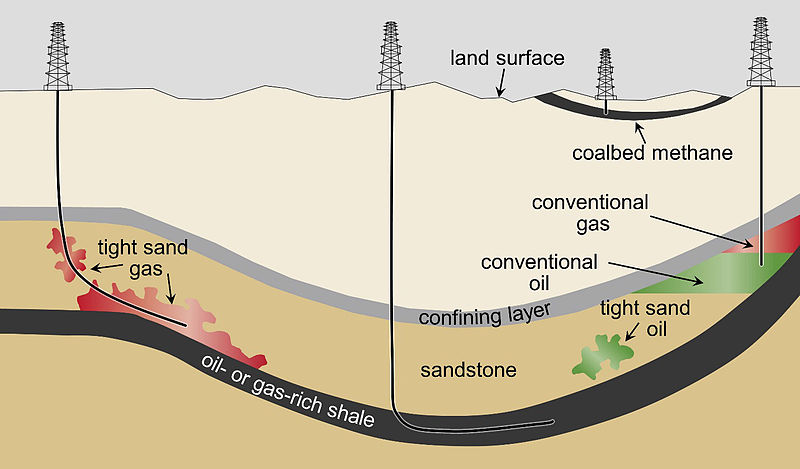
Image source
The study of an unconventional field lies in the production conditions that differentiate it from conventional oil fields, therefore unconventional oil and natural gas fields must be exploited with techniques that differ from conventional fields considering a key geological factor, which is the fact that the oil and natural gas of an unconventional oil and natural gas reservoir accumulates in its formation process its liquid and gaseous phases to the rock structure where there are high capillary forces, all this demands that the engineers in charge of the design in the evaluation and extraction take all the pertinent technical measures.
One of the first comparative considerations is that a conventional oil field has an oil and natural gas formation that can be found and exploited around an average depth of 13,500 feet to 17,000 feet.
This in comparison with non-conventional oilfields, makes that we can get oil at lower depths in non-conventional oilfields, however the oil found in conventional oilfields will be a lighter oil than the oil in non-conventional oilfields, this due to the geological conditions in its formation process.
An influential factor in unconventional reservoirs is the way in which oil and gas migrate from the bottom to the surface in the production process, as some of the oil seeps to the surface, but some is trapped at the bottom.
The normal thing that should happen in a reservoir following the protocols and theories in the way they were formed, is that a conventional reservoir has as oprigen having formed and accumulated in rocks and occupying the space occupied by water in the rocks, and for this it displaces it, making that one of the main characteristics of the rocks of the producing reservoir is high permeability and high porosity, far from this condition what we will find are unconventional reservoirs, which are out of the theory of formation, migration and production of oil that we know more commonly.
The other factor that differentiates an unconventional reservoir from a conventional one is that the production methods and mechanisms of a conventional reservoir allow oil and natural gas to flow from the bottom of the producing wells simply because of the energy of the reservoir itself and the high pore pressure of the producing reservoir rock, as time goes by, this condition loses properties, that is to say, the reservoirs lose that thrust, that energy in the form of pressure is lost, so an artificial lift method is needed for each producing well, among which we can highlight electrosubmersible pumping, mechanical pumping, progressive cavity pumping, artificial gas lift, among others.

Image source
Conclusion
The fluids contained in subsurface formations (oil reservoirs) such as oil and natural gas have certain physical properties that describe their dynamic behavior, these physical properties are permeability, which is the ability of the rock to let oil and natural gas flow between the interconnected spaces of the rock (pore space), also the viscosity of the oil, which is the resistance to flow and move, I mention the properties of the fluids, because these properties are different between conventional and unconventional reservoirs.
At the same time these differences between the properties impact between the ways of extracting oil and natural gas from a conventional and unconventional reservoir, for example in an unconventional reservoir much of that oil has high viscosity, so in order to extract it, it is necessary to heat the formation with steam injection, while a conventional reservoir applies methods under which most of the time the producing well can produce with its own energy, while a conventional well can produce with its own energy, while an unconventional reservoir has high viscosity, so in order to extract it, it is necessary to heat the formation with steam injection, while a conventional reservoir applies methods under which most of the time the producing well can produce with its own energy, while an unconventional well can produce with its own energy.
The origin of the different properties of the rock and fluids lies in the formation process of these hydrocarbons, in some occasions the oil and natural gas was formed geologically in a way to form conventional reservoirs, while in other occasions there were other geological conditions to form unconventional reservoirs.
References
[1] Petroleum Resource Management System (revised June 2018) (1.01 ed.). Society of Petroleum Engineers.
[2] Gluyas, Jon; Swarbrick, Richard (2004). Petroleum Geoscience. UK, USA & Australia: Blackwell Publishing.
[3] Oil Glut, Price Cuts: How Long Will They Last?". U.S. News & World Report. Vol. 89, no. 7. 18 August 1980.
Your posts are always incredibly interesting. Do you work in the fossil fuel extraction industry?
Hello friend, I certainly worked in the oil industry for 4 years as a drilling operations engineer.
wow! It's the first time I've met a drilling operations engineer. It must be a very difficult job. It is a job that requires a very high level of professionalism
Thanks for your contribution to the STEMsocial community. Feel free to join us on discord to get to know the rest of us!
Please consider delegating to the @stemsocial account (85% of the curation rewards are returned).
You may also include @stemsocial as a beneficiary of the rewards of this post to get a stronger support.