Water Treatment "Part 6": Water quality.
Only 0.5% of the total amount of water on Earth is pure water, more than 800 meters below ground level is where the majority of this pure water may be found.
Human activities often cause water pollution, so water becomes a means of transporting waste of many materials as well as transferring heat as a result of its use in cooling. Rivers and seas are used as sewage systems, which has led to pollution of surface waters in most regions of the world, in addition to the severe decrease in the number of aquatic animals and plants. Additionally, analyses frequently revealed that there were quantities of nitrates and pesticides in groundwater, indicating that it was not immune to contamination.
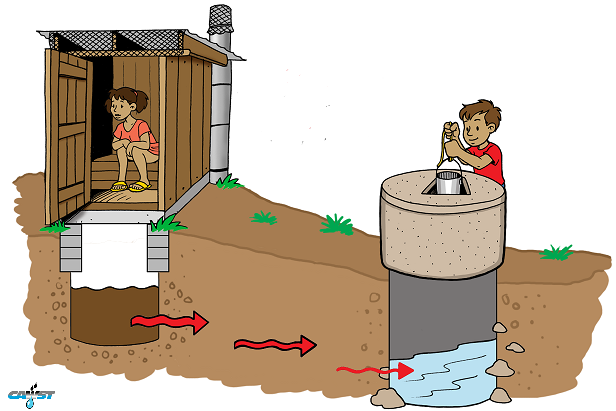
Groundwater Contamination from pit latrines Latin America style
Thermal pollution:
Due to abnormal factors resulting from industrial activities, the surface water temperature has increased. This phenomenon has its pros and cons, and it is called thermal pollution.
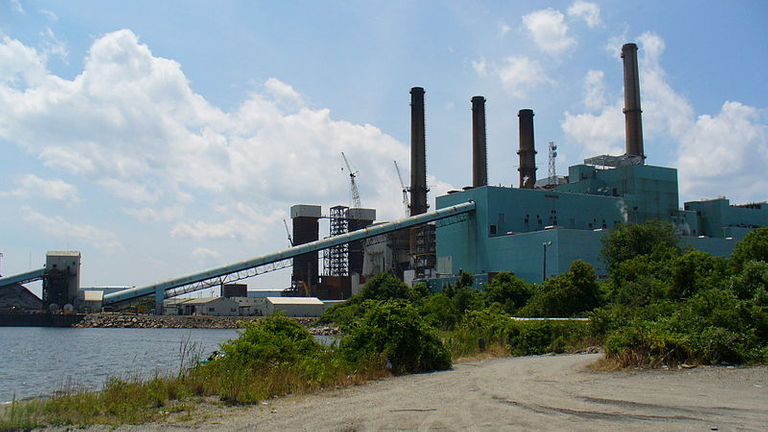

The Brayton Point Power Station in Massachusetts discharged heated water to Mount Hope Bay until 2011. The plant was shut down in June 2017
One of the negative effects of thermal pollution is the decrease in the cooling capacity of the water throughout the summer due to the high temperatures. Also, the decomposition of organic matter and the decrease in oxygen caused by this phenomenon may lead to anaerobic conditions that lead to fish doom during the same season. One benefit of this phenomena is that water does not freeze as quickly during the winter and self-purification processes accelerate as a result of the increased vital activity in the water.
Insoluble substances:
The molecules of an insoluble substance do not dissolve in water. In order to remove these particles from the water, it is vital to know their weight and diameter. Where, to remove particles larger than 10 µm in diameter, sedimentation or flotation is used. The size of the suspended particles is typically considerable, these particles have mineral or organic sources, such as when plants decompose or when sewage or industrial waste are discharged.
Decaying organic matter, animal organisms, faecal matter, and waste from vital industries all belong to the group of floating, insoluble solids that pollute water. Also, in the event that there are high concentrations of phosphate in the water, aquatic plants grow rapidly, and this obstructs the passage of light, so the water becomes anaerobic, and thus the death of marine animals occurs.
It should be noted that plants cause the breakdown of photosynthetic and inorganic compounds in water and are considered an essential component of the natural water cycle, but some of these aquatic plants are classified as toxic. In general, if they are present in moderate proportions, marine plants do not pose any harm to public health.
The ability to grow algae in the water increases due to the discharging of treated wastewater to surface water, so the process of treating it to prepare drinking water becomes very expensive.
As for the insoluble floating liquids, they are the wastes of chemical factories, such as mineral oils that leak from pipeline transport. These mineral oils prevent light and oxygen from entering the water when they form a floating layer on the surface.
Dissolved compounds:
The compounds dissolved in water have a diameter of less than 10 power minus 9 metres. Dissolved gases such as oxygen and nitrogen are present in rainwater, while carbon dioxide is present in groundwater, in addition to the possibility of the presence of hydrogen sulphide and methane gas. It also dissolves in the water many salts and minerals present in the soil. On the other hand, as a result of sewage, significant amounts of salts can enter the water. Between 1 and 10 mg/L is the concentration of organic compounds in surface or ground water.
The dry sediment remaining from water evaporation can be weighed to determine the total dissolved salts concentration, and it can be set directly by the TDS device.
Heavy metals and radioactive compounds are considered microscopic inorganic pollutants that pose a threat to human health if they are present even in very small proportions in water. The same applies to pesticides that are classified as microscopic organic pollutants and are considered very harmful, even if they are present in small amounts.
References:
- Unsafe water kills more people than war, Ban says on World Day". UN News. 22 March 2010. Retrieved 10 May 2018
- Raymond Desjardins- Livre: Le traitement des eaux- 2éme edition- Ecole Polytechnique de Montréal- 1997- ISBN 2-553-00643-8
- Drinking Water Treatment- EDX- Delft University of Technology.
- Book- Drinking Water: Principles and Practices- by Hans J C Van Dijk (Author), Jasper Q J C Verberk (Author), Peter J De Moel.
Thanks for your contribution to the STEMsocial community. Feel free to join us on discord to get to know the rest of us!
Please consider delegating to the @stemsocial account (85% of the curation rewards are returned).
You may also include @stemsocial as a beneficiary of the rewards of this post to get a stronger support.