Water Treatment "Part 18": Disinfection and oxidation with Ozone.
Clear water is produced by the earlier purification steps we covered in this series of water treatment, but this does not imply that it is safe to consume, clarity can conceal harmful contamination such as mineral and chemical compounds or pathogenic bacteria. Therefore, before distributing the water in the transmission systems, the remaining organic components must be removed by oxidation, and bacteria and viruses must be eliminated by sterilisation.
Injecting ozone into water:
Ozone air is produced using a variety of ozonators (ozone-generating equipment), and its ozone content can range from 20 to 10g per cubic metre of air.
The method used to dissolve ozone in water is crucial because it influences the degree of oxidation and sterilisation produced overall as well as the efficiency of oxidation.
When ozone gets injected into water, pollutants including bacteria, viruses, are instantly oxidised and removed. Typically, the liquid can be dispersed in the gaseous phase, but when drinking water is ozonated, 0.5 to 4 grammes of ozone are added to each cubic metre of water for treatment, with ozone levels in the air ranging between 15 and 20 g/m3, there are between 0.025 and 0.25 cubic metres of ozone air flowing per cubic metre of treated water under these circumstances. Since this proportion is so little, ozone is essentially injected into the water medium rather than the other way around. Most often, precise perforations, a water injector, or a revolving turbine are used to infuse ozone air.
Ozone is injected into water by moving through the water medium in the form of tiny bubbles. As a result, there is a lot of interaction between the gaseous and liquid phases, which greatly increases the amount of ozone that dissolves in the water.
Depending on the level of contamination, either a single chamber (figure 1) or a series of chambers (figure 2) are used for the oxidation process. Extending contact time increases the degree of oxidation on the one hand and provides greater sterilisation on the other, which is an advantage of having several chambers.
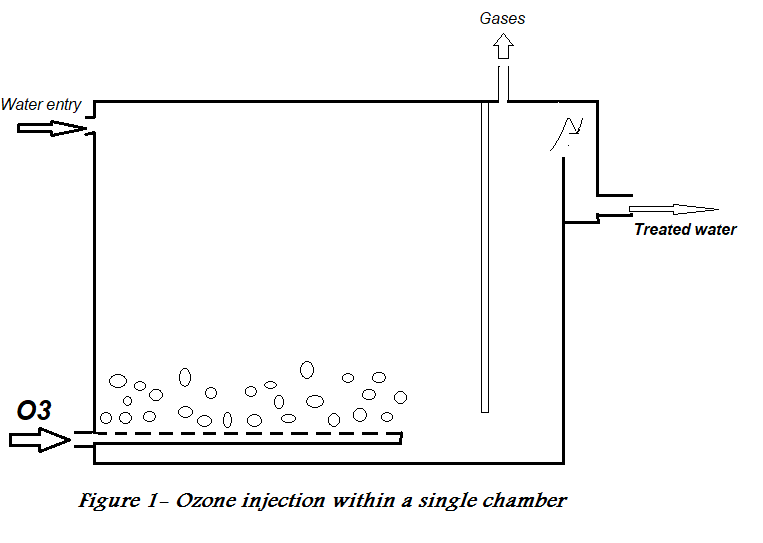
[Made using Microsoft Paint]
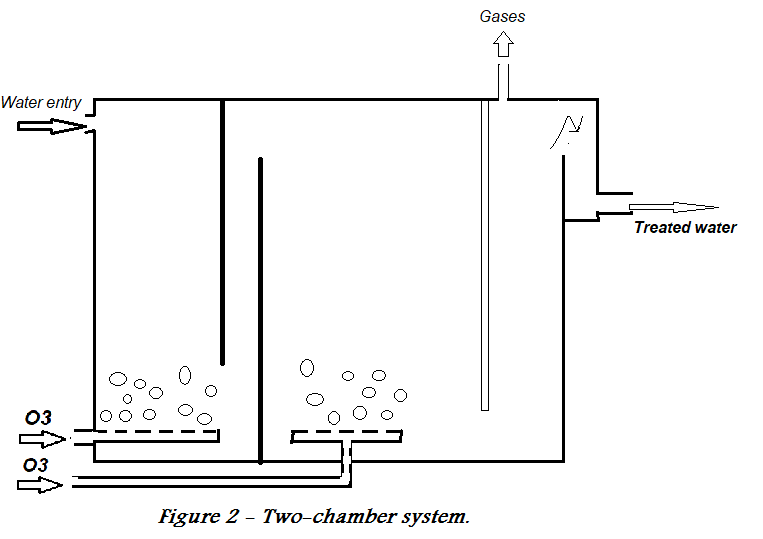
[Made using Microsoft Paint]
Ozone is occasionally exclusively employed as an oxidant, disregarding its sterilising function. In order to improve the yield and attempt to consume the most ozone possible, it is therefore preferable in this situation to utilise the ozone air re-pumping system in the same room or in a different room. With this technique, the ecosystem is protected from ozone emitted into the atmosphere while the yield is increased.
When there is a significant load of suspended materials or high concentrations of sedimentable components render the bubble injection method inapplicable. In these circumstances, a water injector or rotary turbine must be utilised. The round motion of the rotary turbine draws the ozone air and treated water together from the tip of the device, then the mixture is introduced into the treatment chamber. Regarding water injector method, it is based on the idea of water vacuum pumps, where, ozone air is distributed inside the treatment chamber when some of the water to be treated travels through the pump.
Ozone is used in drinking water treatment facilities at different stages of the process, first as an oxidant in the early stages of the treatment process and then as an oxidizer and disinfectant in the final phase of treatment.
References:
- [Introduction to Water Chemistry (Pollution- Treatment- Analysis). Dr. Nasser Al-Hayek. Publication of the Higher Institute for Applied Sciences and Technology (HIAST). Syrian Arab Republic, 2017.]
- Taparhudee, Wara (2002). "Applications of Paddle Wheel Aerators and Diffused-Air System in Closed Cycle Shrimp Farm System" (PDF). Witthayasan Kasetsart (Sakha Witthayasat). 36: 408–419. Retrieved 26 April 2020.
- Unsafe water kills more people than war, Ban says on World Day". UN News. 22 March 2010. Retrieved 10 May 2018
- Raymond Desjardins- Livre: Le traitement des eaux- 2éme edition- Ecole Polytechnique de Montréal- 1997- ISBN 2-553-00643-8
- Drinking Water Treatment- EDX- Delft University of Technology.
- Book- Drinking Water: Principles and Practices- by Hans J C Van Dijk (Author), Jasper Q J C Verberk (Author), Peter J De Moel.
Thanks for your contribution to the STEMsocial community. Feel free to join us on discord to get to know the rest of us!
Please consider delegating to the @stemsocial account (85% of the curation rewards are returned).
You may also include @stemsocial as a beneficiary of the rewards of this post to get a stronger support.